Trade Overview
Mauritius has successfully transitioned from a low-income, agriculture-based economy to a diversified, upper-middle-income economy with a global reach. It serves as a strategic business and financial hub connecting Asia and Africa. The nation's trade profile is characterized by a strong export-oriented manufacturing sector (notably textiles, apparel, and fish preparations), a resilient agricultural base (primarily sugar), and a rapidly growing services export sector, driven by tourism and financial services. While Mauritius is a net importer of goods, particularly machinery, fuel, and food products, it is traditionally a net exporter of services, which helps to balance its overall trade position.

Why Trade with Mauritius?

Mauritius provides preferential and often duty-free access to a global market of billions through a comprehensive network of trade agreements, including with Africa (AfCFTA, COMESA, SADC), Europe (EU & UK EPAs), India (CECPA), and China (FTA).
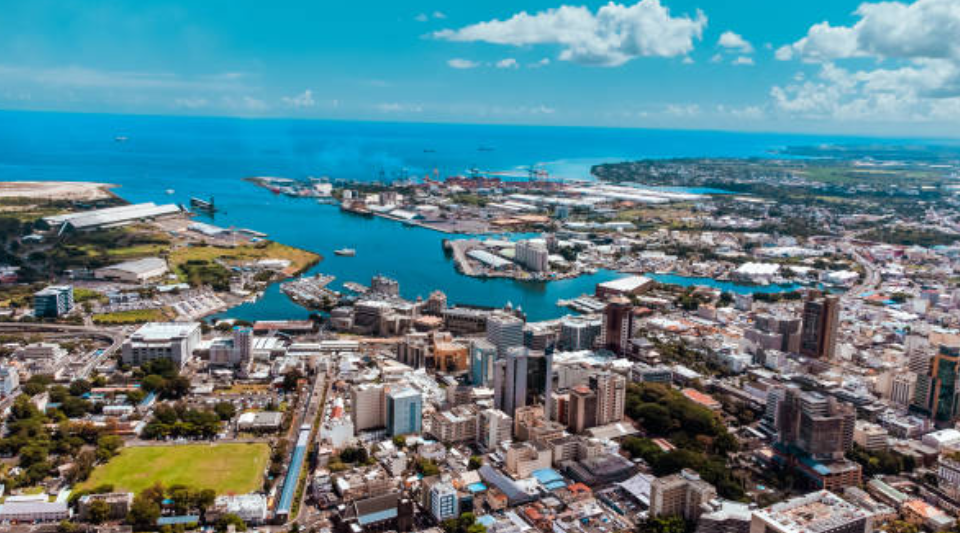

Port Louis is a modern and efficient deep-water port. The Mauritius Freeport offers advanced infrastructure, including cold storage and processing units, with significant tax advantages like a 3% corporate tax rate and exemptions from customs duties and VAT for goods destined for re-export.

The country has a long-standing and sophisticated manufacturing sector, particularly in textiles, apparel, and sugar production, with a growing focus on high-value products.

A key pillar of the economy, the financial services sector facilitates international trade and cross-border investment, particularly into Africa, offering a secure and well-regulated environment.

Mauritius is recognized for its stable democracy, strong governance, robust legal system, and business-friendly environment, providing a predictable and secure platform for international trade.

The workforce is well-educated and fluent in both English (the official language) and French, which is crucial for international business communication and operations.

The country is a significant player in the processing and export of fish and fish preparations, a cornerstone of its goods export basket.
Mauritius: A Premier International Financial and Trade Hub
Mauritius has built its economic success on a foundation of openness, political stability, and a sophisticated, transparent trade and investment framework. Its strategy focuses on positioning itself as a secure and competitive hub for international business, connecting Africa, Asia, and the rest of the world. The policy aims to consolidate existing markets while aggressively pursuing new opportunities through a network of comprehensive trade agreements.
Global & Bilateral Integration:
- World Trade Organization (WTO): As a founding member of the WTO, Mauritius is a strong advocate for a rules-based global trading system and maintains a liberal trade regime.
- Bilateral Agreements:
- China–Mauritius Free Trade Agreement (FTA): China’s first FTA with an African nation, providing duty-free access for over 8,000 products.
- India–Mauritius CECPA: Preferential access for Mauritian goods and services to India’s vast market.
- UK–ESA EPA: Ensures continuity of trade with the UK and maintains preferential market access post-Brexit.
- Turkey–Mauritius FTA: Eliminates duties on a wide range of industrial goods.
Continental & Regional Integration:
- AfCFTA: An early ratifier, Mauritius positions the AfCFTA as a key pillar of its “Africa Strategy,” leveraging its IFC and logistics capabilities.
- SADC: Provides preferential access to Southern African markets under the SADC Trade Protocol.
- COMESA: Duty-free access to a market of over 580 million people via the COMESA FTA.
- Indian Ocean Commission (IOC): Cooperates with island economies (Comoros, Madagascar, Reunion, Seychelles) on trade and development.
Investment & Legal Reforms:
- Economic Development Board (EDB): Acts as a one-stop-shop for investment, trade, and economic development, assisting with permits, incentives, and regulatory requirements.
- Business Facilitation: The Business Facilitation Act streamlines processes and reduces bureaucracy, contributing to Mauritius’ high ease-of-doing-business rankings.
- Advanced Legal Framework: A hybrid legal system combining English common law and French civil law, with the Privy Council (UK) as the highest appellate authority.
Fiscal Regime: Mauritius offers a harmonised 15% tax rate with no capital gains tax, no inheritance tax, and no withholding tax on dividends. Export and global business sectors benefit from additional tax credits.
Mauritius has successfully transitioned from a monocrop economy based on sugar to a diversified, service-driven economy. Its national development strategy emphasises strengthening high-value sectors and expanding new frontiers such as the blue economy and green innovation.
Current Trade Snapshot:
- Primary Exports: Textiles and apparel, tuna and fish products, sugar, and high-value services.
- Key Imports: Machinery, transport equipment, petroleum products, food items, and industrial inputs.
- Re-exports / Transhipment: Rapidly expanding via the Mauritius Freeport, a regional logistics and value-add hub.
Focus on High-Value Sectors:
- Financial Services: A globally recognised IFC supporting cross-border investment, wealth management, and corporate structuring. Mauritius is expected to host the Africa Credit Ratings Agency.
- ICT & BPO: A leading destination for IT, BPO, and knowledge services backed by a skilled, bilingual workforce and world-class telecoms.
- High-End Manufacturing: Rapid growth in medical devices, precision engineering, and luxury goods (jewellery, watches).
- Blue Economy: Leveraging a 2.3 million km² Exclusive Economic Zone for aquaculture, marine biotechnology, high-value fish processing, and deep-ocean water applications.
Mauritius has invested heavily in modern logistics infrastructure and efficient trade processes to reinforce its position as a major regional and international trade gateway.
Port Louis Harbour & Modern Airport:
- Port Louis Harbour: A strategic maritime gateway featuring modern container terminals, with continuous expansion and dredging to handle larger vessels and increased transhipment volumes.
- Sir Seewoosagur Ramgoolam International Airport: Equipped with a modern terminal and a dedicated Freeport cargo and logistics zone enabling efficient air freight movement.
Streamlining Trade Processes:
- Mauritius TradeNet (Single Window): A pioneering electronic system linking customs, ports, and all government trade agencies, enabling digital submission of documents and significantly reducing clearance times.
- Customs Modernisation: The Mauritius Revenue Authority utilises a risk-based clearance system to expedite legitimate trade while ensuring strong compliance controls.
Investment Overview
Mauritius stands out as a premier investment destination in Africa, renowned for its economic competitiveness, political stability, and sophisticated financial ecosystem. Having successfully diversified from its traditional reliance on sugar and textiles, the nation now presents a dynamic, service-oriented economy. The government actively cultivates foreign direct investment through a combination of investor-friendly regulations, attractive incentives, and a strategic focus on high-growth sectors like Financial Services, ICT, Renewable Energy, and the Blue Economy. The Economic Development Board (EDB) acts as a central facilitator, providing a one-stop-shop for investors.

Mauritius Trade & Investment Statistics
$8.9 Billion
Total Trade Volume
Annual goods trade (2023 est.)
90+
Double Taxation Agreements
Extensive global tax treaty network
#1
Africa for Ease of Doing Business
World Bank Ranking (consistently top-ranked in Africa)
>400
Freeport Operators
Companies operating in re-export & logistics hub
15%
Unified Corporate Tax Rate
Flat rate applied across sectors with incentives
>1,000
Global Business Companies
Licensed entities in cross-border investment, fintech, and fund management
Why Invest in Mauritius

Mauritius offers a mature and well-regulated platform for cross-border investment, private banking, wealth management, and global business activities, supported by a network of over 45 double taxation avoidance treaties.
The country leverages its strategic location, trade agreements, and business-friendly environment to position itself as the ideal hub for structuring investments into the fast-growing markets of Africa and Asia.

With a long history of stable democracy and a robust regulatory framework based on international best practices, Mauritius offers a secure and predictable investment climate.

The country provides a low-tax environment, including a harmonized 15% corporate and income tax rate, and a wide array of fiscal incentives such as tax holidays and exemptions in strategic sectors.

With a vast Exclusive Economic Zone of 2.3 million km², Mauritius is actively seeking investment in sustainable fisheries, aquaculture, marine renewable energy, and marine biotechnology.

The real estate sector attracts significant FDI, with numerous schemes for the development of luxury villas, resorts, and commercial properties, often linked to residency permits for investors.

The government is committed to sourcing 60% of its energy from renewables by 2030, creating major opportunities in solar, wind, and waste-to-energy projects.

Mauritius consistently ranks high in global ease of doing business indices, thanks to its streamlined processes for company registration, permitting, and its investor support infrastructure via the Economic Development Board (EDB).
Investment Sectors

Global business structuring, investment funds, private wealth management, insurance, banking, and fintech. The sector is a major contributor to GDP (approx. 14%).

Software development, BPO/KPO services, data centres, disaster recovery, fintech solutions, AI development, and digital services.

Development of luxury hotels, IRS/RES/PDS residential projects, smart cities, business parks, and high-end tourism and wellness facilities.

High value-added manufacturing in textiles, medical devices, pharmaceuticals, jewellery, and precision engineering.

Sustainable fisheries, aquaculture, seafood processing and export, marine renewable energy, and marine R&D.

Investment in solar farms, offshore wind, waste-to-energy plants, and energy efficiency solutions to meet the 60% renewables target by 2030.
Investment Incentives and Support (Facilitated by EDB)
These incentives support regional development, integration, and competitiveness across Southern Africa in alignment with Madagascar's economic cooperation goals.
Tax & Fiscal Incentives
- Corporate Tax: Harmonized 15% rate, with an 8-year tax holiday for companies in targeted tech sectors or those developing intellectual property in medical/pharma sectors. A lower rate of 3% applies to companies engaged in the export of goods.
- Specific Sector Incentives: The Budget 2024–2025 introduced an 80% partial income exemption for companies with a Robotic and AI Enabled Advisory Services license.
- Capital & Assets: 100% tax exemption on gains from the sale of virtual assets and tokens. Accelerated depreciation is available for specific assets like digital and AI-related infrastructure.
- VAT: Exemptions on specific equipment and inputs for strategic sectors.
Premium Investor Certificate (PIC)
- Land Access: For projects exceeding MUR 500 million, the PIC offers a framework for negotiating a custom package of incentives, rebates, exemptions, and guarantees directly with the government, ensuring long-term project viability.
Business & Operational Support
- Premium Investor Certificate (PIC): For projects over MUR 500 million (~$11M USD), the PIC provides a direct negotiation channel with the government for a bespoke package of incentives and guarantees.
One-Stop-Shop Facilitation: The EDB assists with all aspects of company incorporation, licensing, and permitting.
Work & Residence Permits: The EDB facilitates Occupation and Residence Permits for investors, professionals, and their families, with clear pathways linked to investment.
Success Stories
Illustrative examples given the scale of the economy; focus on potential and established niches.
Global Financial & Business Hub
Numerous international banks (e.g., HSBC, Standard Chartered), law firms, and corporate service providers use Mauritius as their regional headquarters and hub for structuring billions of dollars in investment into Africa and India annually.
High-Value Manufacturing & Exports
Companies like AFGRI (focused on agriculture) and ArystaLifeScience use Mauritius as a hub for their African operations, leveraging the country's business-friendly environment and logistical strengths.
Pioneering Real Estate Development
The development of Ebene Cybercity created a dedicated, world-class hub for ICT/BPO companies, attracting global giants and fostering a thriving tech ecosystem.
Madagascar Investment News

Indian Apparel Firm Expands $60M Textile Facility in Madagascar

Major Investment in Green Minerals: Madagascar’s $300M Nickel Project

EU Development Fund Allocates €120M to Madagascar’s Agrifood Sector

Eco-Tourism Gets a Boost: $110M Invested in Madagascar Hospitality Sector
Technology Overview
Mauritius is aggressively positioning itself as a leader in the digital economy of Africa. Underpinned by excellent international connectivity through multiple submarine fibre optic cables and a national strategy for digital transformation ("Digital Mauritius 2030"), the country is fostering a vibrant ecosystem for technology and innovation. The government has established a clear vision to integrate emerging technologies like AI, Blockchain, and IoT across all major economic sectors. This ambition is supported by a strong legal framework, targeted incentives for tech startups, and significant investment in human capital.
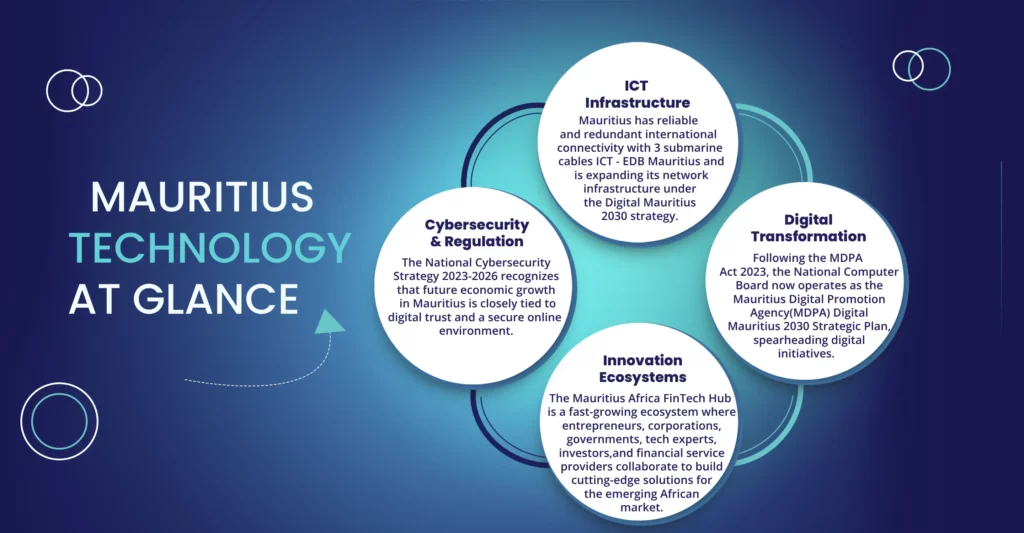
Technology Facts & Figures
Technology Sectors in Mauritius

As a leading African fintech hub, there is a strong focus on developing digital payment solutions, regulatory sandboxes for new products, insurtech, and leveraging blockchain for financial services.

A National AI Strategy is in place, with the Mauritius Artificial Intelligence Council (MAIC) driving adoption. Opportunities are actively promoted in AI for public services, finance, healthcare, and agriculture.

Continued investment in international connectivity (SAFE, LION, METISS cables) and the development of carrier-neutral data centres and cloud services to support the digital economy.

Development of digital marketing platforms, smart hotel management systems, data analytics to understand tourist behaviour, and other technologies to enhance the high-end tourism product.

Leveraging technology for the pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing sectors, including electronic health records and telemedicine solutions.

Driving the digital transformation of public services, including the development of a national digital identity system to create a seamless, paperless administrative environment.

Utilizing technology for sustainable fisheries management (vessel monitoring), marine conservation (drones, GIS), and research in marine biotechnology.
Leading Tech hubs in Mauritius
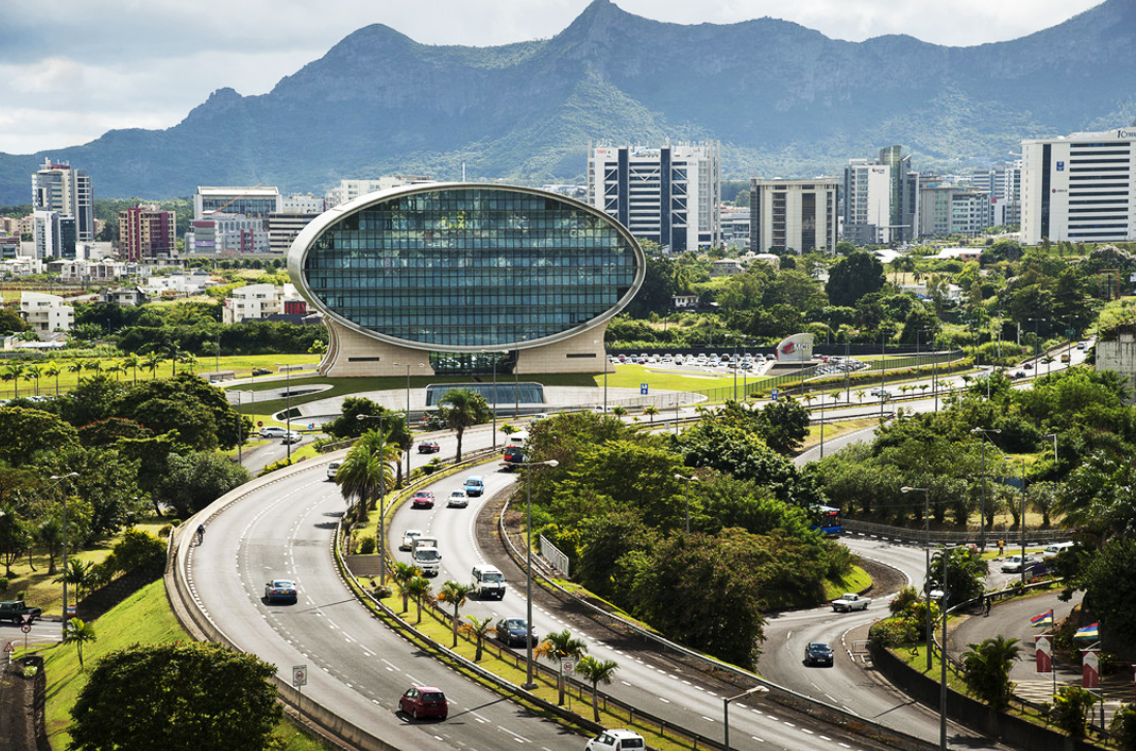

The country's primary technology park, located centrally, which serves as a modern business hub for hundreds of local and international ICT, BPO, and financial services companies. It was the foundational project in establishing Mauritius as a "Cyber Island."

The EDB actively promotes investment into the tech sector through specific incentives, including the Innovator's Occupation Permit, designed to attract tech entrepreneurs and startups to Mauritius.

A key government body that provides grants and support for R&D and innovation across various sectors, including funding for dozens of AI-related projects.

An organization dedicated to fostering a collaborative ecosystem for fintech innovation, connecting startups, corporations, and regulators to drive the future of financial services in Africa.

The government's formal strategy, launched in 2018, and the establishment of the Mauritius Artificial Intelligence Council (MAIC) provide a clear roadmap and regulatory oversight for the ethical and strategic implementation of AI across the economy.

Mauritius offers a Regulatory Sandbox Licence, allowing entrepreneurs to test innovative technologies and business models (especially in fintech) in a controlled environment before full-scale deployment.
Mauritius Technology News

Mauritius Accelerates National AI Strategy with New Research Initiatives

Mauritius FinTech Hub Fosters Startups with Regulatory Sandbox & Investment Support

Ebene Cybercity: The Beating Heart of Mauritius’ Digital Economy

Digital Identity Rollout Boosts E-Government Services in Mauritius
Unlock The Potential Of Mauritius
Mauritius is positioning itself as a dynamic investment destination in the Indian Ocean region, leveraging its strategic location, stable governance, and advanced economic infrastructure. With world-class financial services, a thriving ICT and BPO sector, ongoing investment in logistics and port infrastructure, and a strong focus on sustainability and innovation, the country offers high-potential opportunities in high-end manufacturing, green finance, aquaculture, and the blue economy. Its extensive trade agreements, investor-focused institutions like the Economic Development Board (EDB), and commitment to ease of doing business make Mauritius a compelling choice for international investors and global enterprises.
Contact Us
Ezekiel Tinashe Mukanga
31 Josiah Chinamano Avenue
Harare, Zimbabwe
