
Trade Overview
Malawi is strategically repositioning its economy from a reliance on primary agricultural exports to a value-adding hub for manufacturing and trade within Southern and Eastern Africa. The country is leveraging its strong agricultural base as a foundation for developing sophisticated agro-processing industries. The national trade policy prioritizes export diversification and integration into regional value chains, aiming to transform raw materials into finished goods for both regional and international markets. As a land-linked country bordered by key markets, Malawi offers a logistical nexus for trade flowing through the SADC and COMESA regions, with a clear focus on building industrial capacity to serve these corridors.

Why Trade with Malawi?

Malawi’s membership in SADC, COMESA, and AfCFTA provides access to a combined market of over 1.3 billion people and ideal supply chain routes into Tanzania, Zambia, and Mozambique.

Malawi’s agriculture includes tea, tobacco, legumes, oilseeds, and sugarcane, offering significant opportunities for value addition into processed export products.

The government is promoting investment in light manufacturing—textiles, garments, food & beverage production—boosting regional supply chain integration.

Malawi offers a large, youthful, competitive workforce suitable for labour-intensive industries and export-oriented processing operations.

Malawian exports are eligible for duty-free access to the EU (EBA) and preferential access to the US under AGOA (currently pending renewal).

Malawi continues improving road & rail networks and introducing One-Stop Border Posts to reduce logistics costs and improve transit times.
Malawi: Unlocking a Diversified Gateway for Global Trade
Malawi is actively implementing policies to diversify its economy beyond its traditional reliance on agriculture, create an attractive and transparent investment climate, and deepen its integration with regional and global markets. The overarching goal, as articulated in long-term plans like the Malawi Vision 2063, is to transform the nation into an inclusively wealthy and self-reliant industrialized country. A key strategy is to use trade as a tool for structural transformation, building a robust productive base, and moving up the value chain.
- World Trade Organisation (WTO): As a member of the WTO, Malawi is integrated into the global rules-based trading system, which governs its trade relations with numerous partners.
- Bilateral Agreements: Malawi maintains several bilateral trade agreements to enhance economic ties. Key agreements include those with South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Botswana. A customs agreement with Botswana, dating back to 1956, allows for duty-free trade of most goods originating in either country.
- AfCFTA (African Continental Free Trade Area): Malawi has ratified the AfCFTA Agreement and views it as a critical framework for unlocking its export potential. The National Export Strategy II specifically prioritizes capitalizing on the continent-wide market to achieve its diversification goals.
- SADC (Southern African Development Community): As a member of SADC, Malawi benefits from preferential access to a large regional market through the SADC Trade Protocol.
- COMESA (Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa): Malawi is a founding member of the COMESA Free Trade Area (FTA), which provides for duty-free trade among member states, facilitating smoother trade with key regional partners like Kenya.
- Malawi Investment and Trade Centre (MITC): The primary government agency acting as a one-stop shop to promote and facilitate investment and exports. Established by the Investment and Export Promotion Act of 2012, MITC provides services such as project appraisal, site identification, assistance with permits, and joint venture facilitation.
- Investment Freedom: The Constitution of Malawi guarantees the freedom to invest and own property. Foreign investors are generally granted national treatment with no restrictions on ownership or sector, allowing for 100% foreign ownership in most areas. However, foreign participation in a company's Initial Public Offering (IPO) is limited to a 49% aggregate stake, a restriction that does not apply to subsequent trading.
- Malawi's tariff policy is based on the SADC and COMESA common external tariffs. All imports must be declared, with duties calculated based on the Cost, Insurance, and Freight (CIF) value of the goods.
- Industrial Policy Focus: Key sectors for import substitution include wood products, leather goods, and pharmaceuticals, suggesting strategic tariff use to encourage local production.
- Maximum tariff rate: 25%.
Malawi is implementing a clear strategy to transition from an exporter of raw agricultural commodities to a producer and exporter of value-added goods and services. This is a central pillar of the Malawi Vision 2063 and the National Export Strategy II (NES II), which aim to make Malawi a competitive and sustainable sourcing destination.
Current Trade Snapshot:
- Primary Exports: The economy is heavily reliant on a few key agricultural products. Tobacco is the dominant export, followed by groundnuts, tea, and dried leguminous vegetables. This narrow export base makes economic diversification a critical national priority.
- Key Imports: Major imports include petroleum products, fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and second-hand clothing. This highlights significant opportunities for import substitution through local manufacturing and production.
- Agriculture & Agribusiness
- Potential: Agriculture is the backbone of the economy, and the government's strategy focuses on commercialisation, diversification, and value addition. The goal is to move beyond exporting raw tobacco, tea, and sugarcane to processing these into higher-value products and developing other value chains like oilseeds and horticulture.
- Value Addition: The vision emphasises the growth of agro-based industries to create jobs and provide a ready market for agricultural produce.
- Mining – Beyond Extraction
- Untapped Potential: Malawi possesses significant mineral resources, including rare earth elements, uranium, niobium, and bauxite. The mining sector is identified as a key driver for industrialisation.
- Value Addition: Recent developments show a strategic push to ensure value is captured domestically. For instance, the Kanyika Niobium Project has secured an offtake agreement for its output, signalling market confidence. Similarly, off-take deals have been signed for rare earths from the Songwe Hill project and uranium from the Kayelekera mine, with the government securing equity stakes in these projects.
- Manufacturing Growth
- Industrialisation Pillar: Industrialisation is a core pillar of Malawi Vision 2063, aiming to build a resilient and self-sufficient economy.
- Import Substitution: The National Industrial Policy explicitly targets import substitution in sectors like pharmaceuticals, wood products, and leather goods to reduce reliance on imports and build domestic capacity. The NES II also prioritizes enhancing the competitiveness of "Made in Malawi" products for regional and global markets.
As a land-linked country, Malawi's trade competitiveness is heavily dependent on efficient transport and logistics. The government is focused on leveraging key regional corridors and modernizing trade systems.
- The Nacala and Beira Corridors: A Regional Lifeline
- Strategic Gateways: These corridors are Malawi's most critical routes to the sea, connecting it to the ports of Nacala and Beira in Mozambique. They are essential for transporting the country's main exports, such as tobacco and tea, to international markets.
- Impact: The efficiency and development of these corridors directly impact transport costs and trade volumes. High transport costs can significantly reduce the competitiveness of Malawian products. Development efforts within these corridors aim to improve infrastructure and streamline logistics to boost trade.
- National Single Window: Malawi officially launched its National Single Window system in May 2025. This electronic platform allows traders to submit all regulatory documents through a single portal, aiming to dramatically reduce clearance times, cut costs, and increase transparency. The system integrates with the Malawi Revenue Authority's ASYCUDA World system and is being rolled out in phases, with a plan to include 22 government agencies by September 2025.
- Customs Modernisation: In partnership with the Global Alliance for Trade Facilitation, a new licensing framework and training for customs clearing agents has already resulted in a 16.2% reduction in customs processing time and a 43.2% decrease in documentation errors, improving the speed and reliability of cross-border trade.
Malawi Trade News

Malawi Signs New Regional Trade Agreement to Boost Agricultural Exports

Malawi Tobacco Exports Surge 30% Following New Trade Partnerships

Lilongwe-Nacala Transport Corridor Upgrade to Cut Malawi Export Costs by 25%

Malawi Launches Digital Trade Platform to Connect Farmers with International Markets
Investment Overview
Lesotho offers a unique and stable platform for investors seeking to establish highly competitive, export-focused manufacturing operations. The kingdom's key advantages lie in its deep integration with the South African economy and its preferential access to the US market under AGOA. The government is committed to building upon its success in textiles by diversifying into other light manufacturing and agro-processing sectors. The LNDC provides a one-stop-shop for investors, offering attractive incentives and world-class industrial infrastructure to support the establishment and growth of new enterprises.

Malawi — Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Statistics
FDI inflows remain low and volatile, constrained by macroeconomic instability, foreign exchange scarcity, and persistent infrastructure bottlenecks.
$166 M
FDI Inflow (Realized)
The Reserve Bank of Malawi reports modest inflows reflecting structural weaknesses and subdued investor confidence.
2.0%
FDI Inflow (% of GDP)
A low but stabilizing ratio, signaling limited but ongoing external investment activity.
11.2%
Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Malawi’s investment rate has been declining, indicating reduced capital expenditure in long-term productive sectors.
Agriculture & Mining
FDI Concentration
FDI is concentrated in agriculture, agro-processing, mining, and energy—sectors where Malawi has export potential.
Top 5 Investors (By Sectoral Focus)
- 🇿🇦 South Africa — retail, telecoms, and financial services.
- 🇬🇧 United Kingdom (UK) — long-standing investment in tea and tobacco estates.
- 🇮🇳 India — agriculture, sugar estates, and manufacturing.
- 🇺🇸 United States (US) — agricultural commodity trade and development financing.
- 🇨🇳 China — infrastructure, construction, and small-scale mining projects.
Malawi’s FDI profile is shaped by historical ties, regional influence, and investment in primary commodities.
Where is the FDI Going? (Top Sectors)
-
Agriculture & Agro-Processing
Rank 1
Tobacco, tea, and sugar processing form the backbone of Malawi’s export economy.
-
Mining & Energy
Rank 2
Uranium, rare earths (incl. niobium), solar farms, and hydropower expansion.
-
Financial Services
Rank 3
Banking and insurance driven by regional players (e.g., South African firms).
-
Manufacturing
Rank 4
Small-scale production and light manufacturing, particularly agro-based value addition.
Sources: Reserve Bank of Malawi (2023), World Bank (2024), IMF, UNCTAD.
Why Invest in Malawi

South Africa has a well-established constitutional democracy with strong property rights and an independent judiciary. Its stable legal framework provides investor confidence and protection against arbitrary policy changes.

Malawi's tourism sector has room for expansion, with opportunities in developing accommodation, eco-tourism, and related services.

Membership in COMESA and SADC provides access to a wider market for goods and services.

The Malawian government is taking steps to attract investment through policy reforms and incentives.
Key Investment Sectors in Malawi

Key crops include tobacco, tea, sugarcane, maize, and cotton.

Primarily focused on food processing, beverages, textiles, and cement.

Potential for growth in lake tourism, wildlife tourism, and cultural tourism.

Malawi is working to expand its energy sector, including renewable energy sources.

Opportunities exist in expanding lake-based aquaculture and inland fish farming.

Telemedicine, mobile health apps, and medical devices are transforming healthcare delivery across the country.
SADC-Aligned Investment Incentives in Malawi
These incentives support regional development, integration, and competitiveness across Southern Africa in alignment with Malawi's economic cooperation goals.
Tax Incentives
- Reduced corporate tax rates in Special Economic Zones
- R&D tax incentives (up to 150% deduction)
- Accelerated depreciation allowances
- Employment tax incentives
Financial Support
- Black Industrialist Scheme
- Critical Infrastructure Programme
- Manufacturing Competitiveness Enhancement Programme
- Export Marketing & Investment Assistance
Business Support
- One-stop shop for investors
- Special Economic Zones
- Industrial Development Zones
- Skills development programs
Success Stories
These sectors reflect South Africa’s strategic positioning in regional and global value chains, aligned with SADC development goals.
Automotive Manufacturing
Major global automotive manufacturers including Volkswagen, BMW, Toyota, and Mercedes-Benz have established production facilities in South Africa, exporting vehicles to over 100 countries worldwide.
Renewable Energy
South Africa's REIPPPP has attracted over $20 billion in private investment for renewable energy projects, creating thousands of jobs and adding significant clean energy capacity to the grid.
Business Process Outsourcing
South Africa has become a preferred destination for BPO services, with companies like Amazon, IBM, and Teleperformance establishing major operations centres serving global clients.
Investment News


Building the Future: Sustainability, Innovation, Blue Economy, and Digital Transformation in SADC

EAC–SADC Business Forum

USA TODAY Report Highlights Key Economic Sectors in SADC
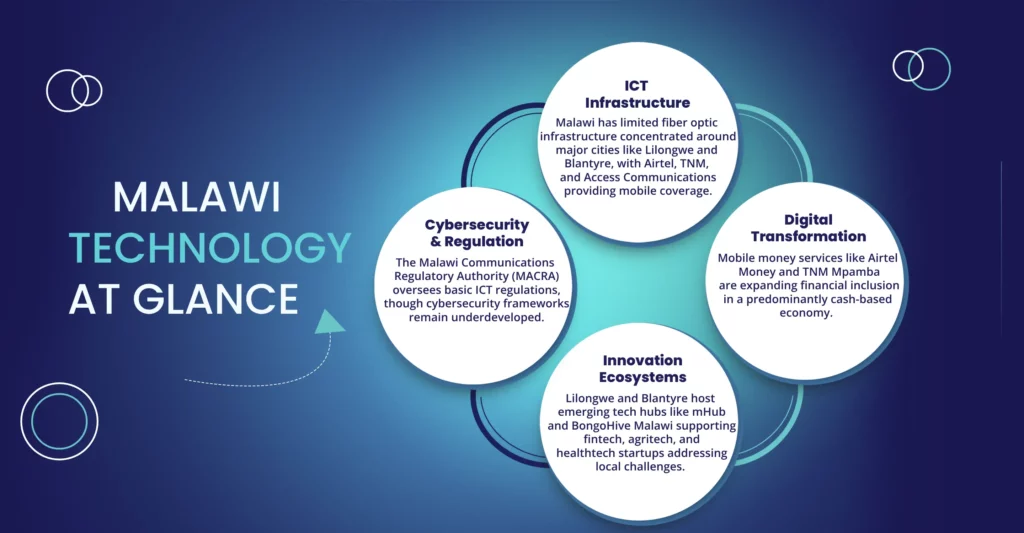
Technology Facts & Figures
Technology Sectors in Malawi

This dominant sector drives financial inclusion through innovations in digital payments, mobile banking, lending platforms, and neo-banking.

This sector employs technologies like AI, telemedicine, and wearables to enhance healthcare accessibility and efficiency.

Driven by mobile and internet penetration, this sector includes online shopping and digital retail solutions.

Uses AI, drones, IoT, and biotech to optimize farming and address food security.

Focuses on solar power, energy storage, and smart grids to enhance energy access.

Being adopted across sectors to enhance productivity and automate tasks.

IoT solutions are revolutionizing homes, businesses, and agriculture with smart monitoring and automation.

Addresses growing cyber risks with demand for security products and skilled professionals.

A rising sector powered by mobile usage and immersive media like AR and VR.
Malawi's Emerging Technology Hubs
As the capital city, Lilongwe is the center of government and business activity, and it's also where most of the country's tech initiatives are based. There is a growing focus on:
>>> E-government services
>>> AgriTech solutions
>>> FinTech development

As the commercial capital, Blantyre is another important center for technology in Malawi. It has a concentration of businesses and industries, driving demand for tech solutions. Key areas include:
>>> FinTech
>>> Logistics and trade-related technologies
Malawi's Leading Tech Hubs
A growing network of innovation spaces across Malawi, supporting startups, digital skills, and entrepreneurship.
Mzuzu E-Hub
18NxtGen Labs (Lilongwe)
25mHub (Lilongwe)
32Polytechnic Innovation Hub (Blantyre)
15Chanco Innovation Hub (Zomba)
12Malawi Technology News

Malawi to Launch First AI and Innovation Hub in Lilongwe

Telekom Networks Malawi Announces 5G Rollout in Major Cities
Malawi’s Digital Economy Project Targets Youth Empowerment and SMEs

Fintech Startups in Malawi Drive Financial Inclusion via Mobile Platforms
Unlock The Tech Potential Of Malawi
Malawi holds significant untapped tech potential driven by a growing youthful population, increasing mobile and internet penetration, and a rising interest in digital entrepreneurship. With expanding access to affordable smartphones and mobile networks, the country is poised to benefit from innovations in fintech, agritech, and e-learning. Government and private sector efforts to improve ICT infrastructure and digital skills training are creating a foundation for a thriving tech ecosystem that can boost economic development, enhance service delivery, and create job opportunities across various sectors.
Unlock The Potential Of Malawi
Malawi offers a dynamic and growing market with significant potential for businesses engaged in international trade. By taking advantage of the benefits offered by regional trade agreements, businesses can expand their operations, enhance competitiveness, and contribute to the country's broader economic transformation.
Contact Us
Ezekiel Tinashe Mukanga
31 Josiah Chinamano Avenue
Harare, Zimbabwe
📞 +263 777 768 425
✉️ info@sadcsotip.com
🌐 www.sadcsotip.com
