
Why Trade with Tanzania

The Port of Dar es Salaam and the country's central corridor provide the most efficient trade route for Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the DRC, Zambia, and Malawi.

Tanzania is uniquely positioned as a member of both the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern African Development Community (SADC), offering businesses preferential access to two of Africa's largest trading blocs.

With a vast and diverse agricultural sector, Tanzania offers immense opportunities to source and process high-quality food products, including cashews, coffee, tea, oilseeds, and pulses, for the global market.

The government's industrialisation drive is creating new opportunities to source locally manufactured goods, including construction materials, consumer products, and processed foods.

Beyond agriculture, Tanzania's significant coastline and lakes support a growing fisheries sector, with opportunities for sourcing processed fish and other seafood products.

The government is actively working to improve the ease of doing business, streamline regulations, and enhance trade facilitation through investments in port efficiency and transport infrastructure.
Tanzania: A Strategic Gateway for East and Central Africa
Tanzania's trade policy is fundamentally linked to its national vision of becoming a semi-industrialised, middle-income country, as outlined in its Five-Year Development Plans (FYDPs).
The strategy is centred on leveraging its strategic geographical location to become a premier trade and logistics hub for East and Central Africa. Key objectives include:
- Promoting export-led growth through industrialisation
- Adding value to agricultural and mineral products
- Using trade to create jobs and foster inclusive development
- Improving the business environment to attract investment
Global & Bilateral Integration:
- WTO: Member of the global rules-based trading system.
- EPAs: Has not signed the EU EPA but benefits from EBA (duty-free, quota-free access to EU for all exports except arms).
Continental & Regional Integration:
- AfCFTA: Ratified and aligned with industrialisation goals.
- EAC: Founding member of a customs union and major destination for manufactured goods.
- SADC: Provides preferential market access to Southern Africa.
- Tanzania Investment Centre (TIC): One-stop shop for investors, assisting with permits, incentives, and business support.
- New Investment Act (2022): Streamlines procedures, enhances investor protection, and aligns legal framework with national goals.
- Export Processing Zones Authority (EPZA): Manages SEZs/EPZs offering fiscal incentives for export-focused manufacturing.
Tanzania is transitioning from raw material exports to processed and manufactured goods by leveraging natural resources.
Current Trade Snapshot:
- Exports: Gold, cashews, coffee, cotton.
- Imports: Petroleum, machinery, vehicles, food — opening opportunities for import substitution.
Focus Areas:
- Mining: Increasing domestic processing of gold, diamonds, Tanzanite, and coal.
- Agriculture: Promoting cashew, coffee, and cotton value chains (e.g. roasting, textiles).
- Blue Economy: Coastal and inland fisheries, aquaculture, and onshore fish processing for export.
Central Corridor & Port of Dar es Salaam:
- Gateway: Serves six landlocked countries (Zambia, DRC, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Malawi).
- Impact: Port efficiency directly affects regional trade and Tanzania’s transit hub status.
- SGR Railway: Modern high-speed rail connecting the port to the hinterland.
Streamlining Trade:
- National Single Window: TNSW enables digital submission of trade documents for faster clearance.
- Customs Modernisation: TRA is aligning with international standards to improve border efficiency.
- Port Development: DMGP is expanding berths, modernising terminals, and increasing cargo throughput.

Tanzania Trade & Investment Statistics
$2.3 Billion
Total Trade Volume
Annual goods trade (2023 est.)
65%
Trade with South Africa
South Africa remains Tanzania's top trade partner
#1
Gold Exporter
Top African exporter of gold to global markets
3
Strategic Corridors
Dar es Salaam, Central & Tanga transport routes
80%
Manufactured Goods
Share of exports that are value-added products
>1,000
Registered Exporters
Active firms supported by TIC & TRA
Why Invest in Tanzania

With vast tracts of arable land and favourable climates, Tanzania is a prime destination for large-scale commercial agriculture and, more importantly, value-added agro-processing (e.g., cashew processing, instant coffee plants, edible oil refining).

Leverage Tanzania's membership in the EAC, SADC, and AfCFTA to establish a manufacturing base to serve over a billion people with preferential tariffs.

With a population of over 65 million, Tanzania offers a significant internal market for locally produced consumer goods, food products, and construction materials.

Invest in the logistics, warehousing, and transport services needed to support the bustling Port of Dar es Salaam and the country's vital transport corridors.

The government offers designated zones with superior infrastructure and attractive fiscal incentives, including a 10-year corporate tax holiday, to encourage investment in manufacturing and export-oriented industries.

Tanzania is home to iconic natural wonders like the Serengeti, Mount Kilimanjaro, and Zanzibar, offering unparalleled opportunities for investment in hotels, lodges, and tourism services.
Key Investment Sectors in Tanzania

Large-scale processing of cashews, coffee, tea, sugar, and oilseeds. Manufacturing of fertilizers, textiles (from local cotton), and leather goods (from local hides).
Production of cement, steel, plastics, and other construction materials. Manufacturing of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG), pharmaceuticals, and assembly of vehicles and electronics.

Development of industrial parks and SEZs. Investment in transport and logistics services, warehousing, and cold chain solutions to support trade through the Dar es Salaam port.

Construction and management of hotels, resorts, and safari lodges. Investment in tourism and hospitality training centres and related supply chains.

Development of power generation projects (gas, hydro, solar, wind). Investment in rural electrification and the manufacturing of energy components.
Investment Incentives and Support (Facilitated by EIPA)
These incentives support regional development, integration, and competitiveness across Southern Africa in alignment with Eswatini's economic cooperation goals.
Tax & Fiscal Incentives
- SEZ/EPZ Incentives: 10-year exemption from corporate tax and withholding taxes on dividends and interest. Exemption from all local government taxes and levies.
- Capital Allowance: 100% capital allowance on industrial buildings, plant, and machinery. .
- VAT:VAT deferment on project capital good.
Specific Examples of Incentives
- Strategic Investor Incentives: For investments over $50M, investors can negotiate a bespoke package of additional fiscal and non-fiscal incentives with the government.
- Duty-Free Imports: Capital goods and raw materials for export production are exempt.
Business & Operational Support
- One-Stop Centre: The TIC provides a comprehensive one-stop service, facilitating company registration, work permits, land acquisition, and access to other necessary licenses.
- Land Access:TIC manages a land bank and assists investors in identifying and securing suitable land for their projects.
Success Stories
Illustrative examples given the scale of the economy; focus on potential and established niches
Regional Beverage Giant
Tanzania Limited (MeTL Group) is a homegrown success story that has grown into a massive conglomerate with operations in manufacturing (textiles, plastics, food processing), agriculture, and logistics, demonstrating the potential of the domestic market.
Industrial Conglomerate
The Royal Eswatini Sugar Corporation (RES) is a world-class sugar producer that has diversified into downstream activities, including ethanol production and electricity co-generation, showcasing a successful model of agricultural value addition.
Port Logistics
DP World is engaged in enhancing the efficiency of the Dar es Salaam port, investing in modernizing berths and improving cargo handling operations to strengthen its role as a premier gateway for regional trade.
Tanzania Investment News

Tanzania Tech Startups Secure $50M in Series A Rounds

Government Expands ICT Infrastructure to Support Digital Economy

New AI Innovation Hub Launched in Dar es Salaam

Microsoft Partners with Tanzanian Universities to Boost Tech Skills
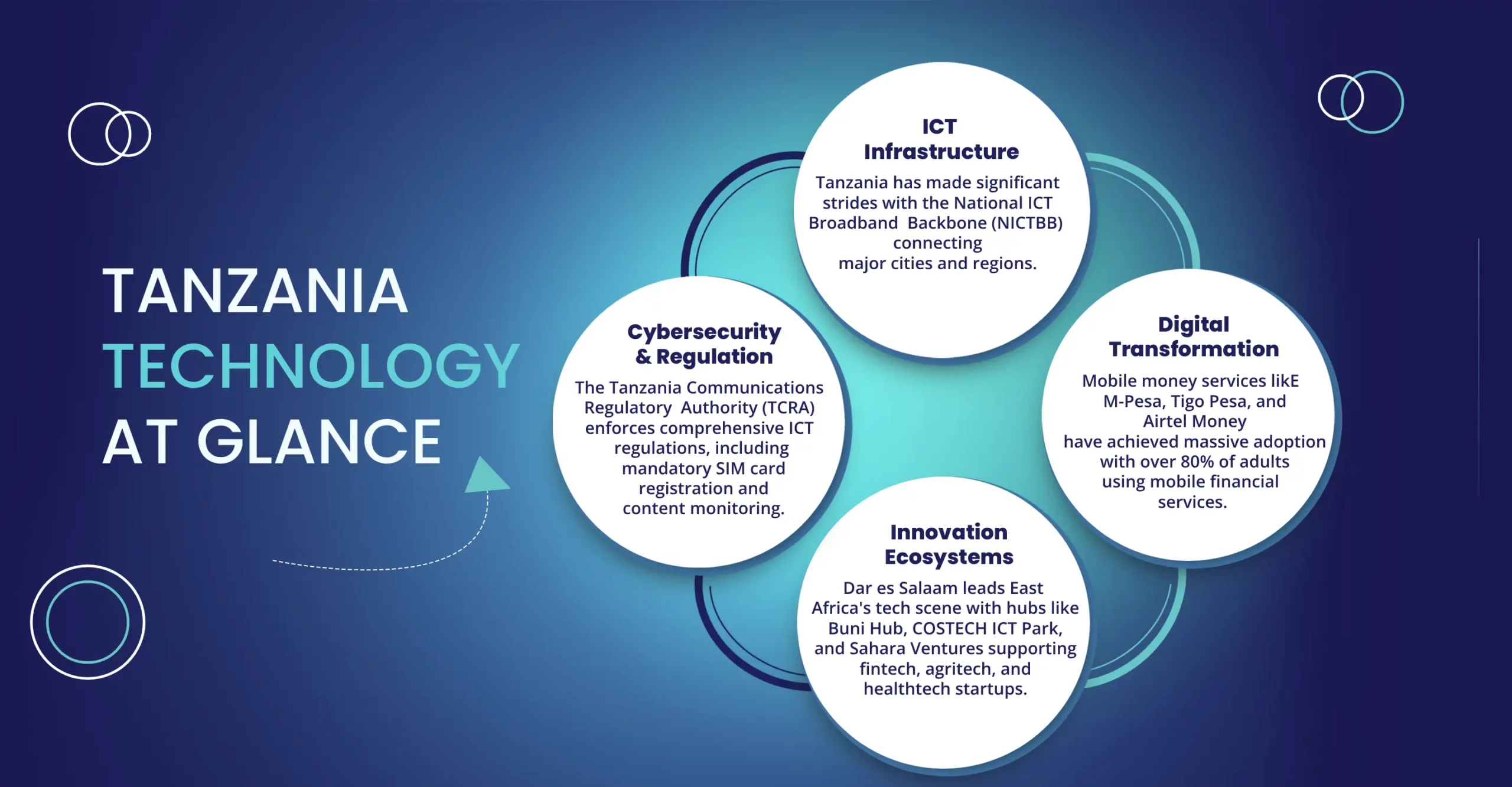
Tanzania Tech Investment Statistics
Key Technology Sectors in Tanzania

Tanzania's most advanced tech sector. Vast opportunities exist in building on mobile money infrastructure to deliver digital insurance, SME lending, and cross-border payment solutions.

Mobile solutions helping smallholder farmers access weather updates, market prices, credit, insurance, and market linkages within national and regional supply chains.

Enabling telemedicine for rural-urban connection, electronic health records, and mobile tools for community health workers to improve access and efficiency in healthcare delivery.

Technology innovations to improve logistics and transport systems, such as port management, cargo tracking, and digital platforms linking truckers with cargo owners.

Localized digital educational content delivered via mobile platforms to reach Tanzania's growing youth population and improve learning outcomes.

Digital platforms for online business registration, tax payments, and other public services are being developed as part of the national digital transformation agenda.
Leading Technology Hubs & Initiatives in Tanzania

As Tanzania’s commercial capital, Dar es Salaam hosts major tech hubs like COSTECH, Buni Hub, and Sahara Ventures, offering incubation, acceleration, and coworking spaces for startups.

A key government body that coordinates and promotes research and technology development across Tanzania, playing a central role in building the national innovation ecosystem.

UCSAF expands ICT services to rural and underserved communities, ensuring broader access to the digital economy through strategic public-private partnerships.

This policy guides ICT sector development, emphasizing infrastructure expansion, human capital, cybersecurity, and creation of local digital content and applications.

Vodacom, Tigo, and Airtel are at the heart of Tanzania's innovation landscape—driving the fintech boom and supporting startups through partnerships and mobile money platforms.
Tanzania Technology News

Tanzania Unveils E-Government Rollout to Streamline Public Services

Fintech Boom in Tanzania: Mobile Platforms Drive Financial Innovation

Tanzania Accelerates 5G Rollout with Major Infrastructure Investments

AgriTech Expands in Tanzania: Farmers Use Apps to Boost Yields
Unlock The Potential Of Tanzania
Tanzania is rapidly emerging as a trade and investment powerhouse in East and Central Africa. Its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and commitment to industrialisation make it a compelling destination for global investors. With growing investments in logistics, energy, agro-processing, mining, and the blue economy, Tanzania offers lucrative opportunities supported by modern infrastructure, investor-centric policies, and a young, dynamic workforce.
Contact Us
Ezekiel Tinashe Mukanga
31 Josiah Chinamano Avenue
Harare, Zimbabwe
📞 +263 777 768 425
✉️ info@sadcsotip.com
🌐 www.sadcsotip.com
